Sustainability is a complex and multifaceted goal, with numerous obstacles hindering its achievement. These challenges, including population growth, resource depletion, and climate change, are interconnected and complex, requiring comprehensive solutions to ensure a balanced and enduring relationship between humanity and the Earth.
Population Growth
Increasing Numbers
The world’s population is increasing at an unprecedented rate. In less than a century, it has grown from 2 billion to over 7 billion people. This rapid increase exacerbates the pressure on natural resources and ecosystems.
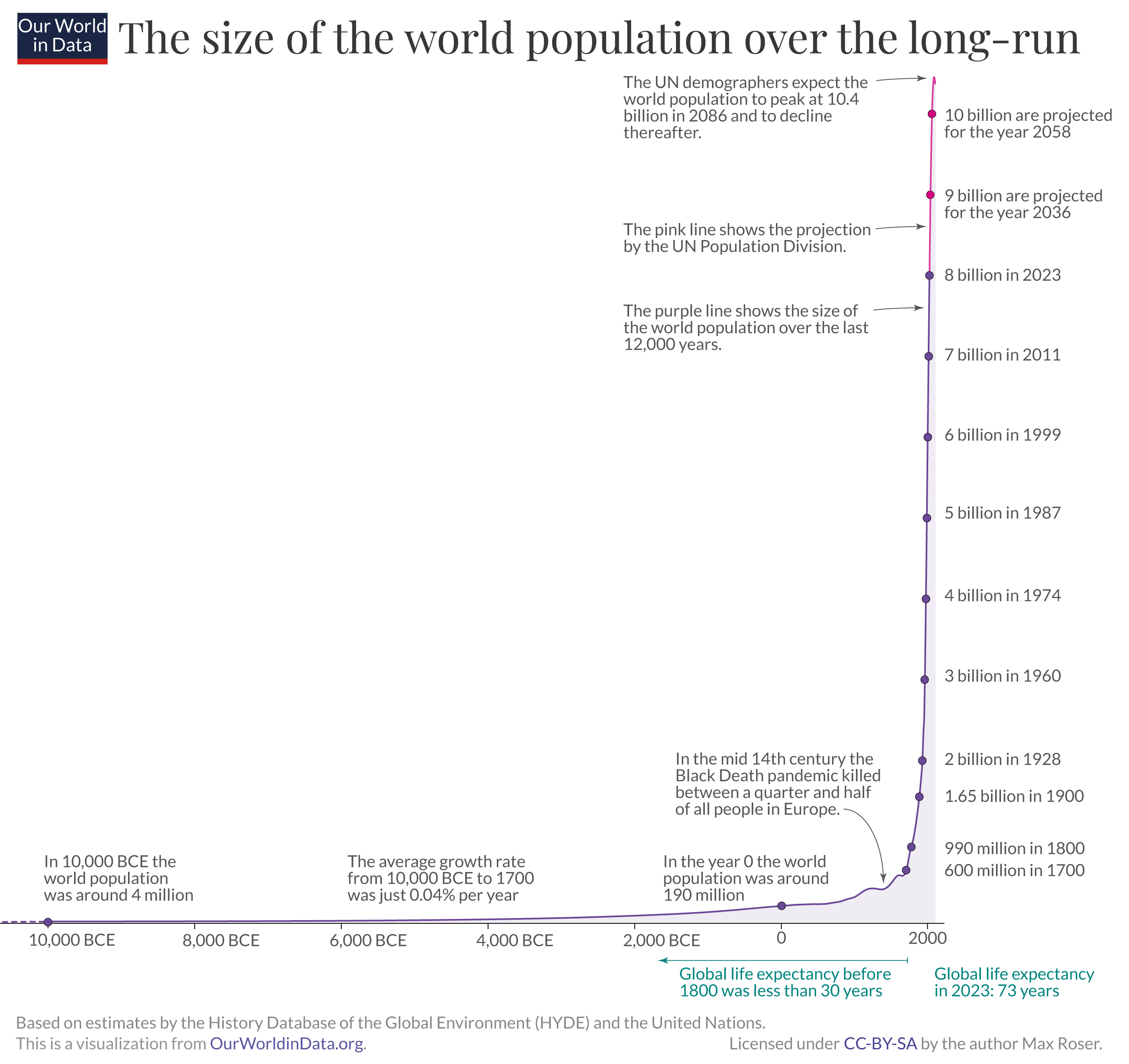
World population has risen extremely rapidly in the last two centuries, intensifying demand for food, water, energy and land. The long-run perspective highlights how recent and steep this growth is compared with most of human history. Source.
Resource Strain: The increased population means a heightened demand for food, water, energy, and other essential resources. This strain is leading to a rapid depletion of resources, escalating the urgency to find sustainable alternatives.
Waste Generation: An increased population leads to more waste production, including plastics, chemicals, and greenhouse gases. The management and disposal of this waste are becoming increasingly complex and challenging.
Urbanisation
Urbanisation is a direct consequence of population growth. As the population grows, urban areas expand, leading to a set of unique challenges.
Infrastructure: Many cities are not equipped to handle the rapid influx of inhabitants, leading to inadequate housing, transportation, and waste management systems. The strain on infrastructure can lead to decreased quality of life and increased pollution.
Environmental Degradation: Urban areas often suffer from air and water pollution, noise, and the heat island effect. These environmental issues can lead to health problems for the inhabitants and damage the surrounding ecosystems.
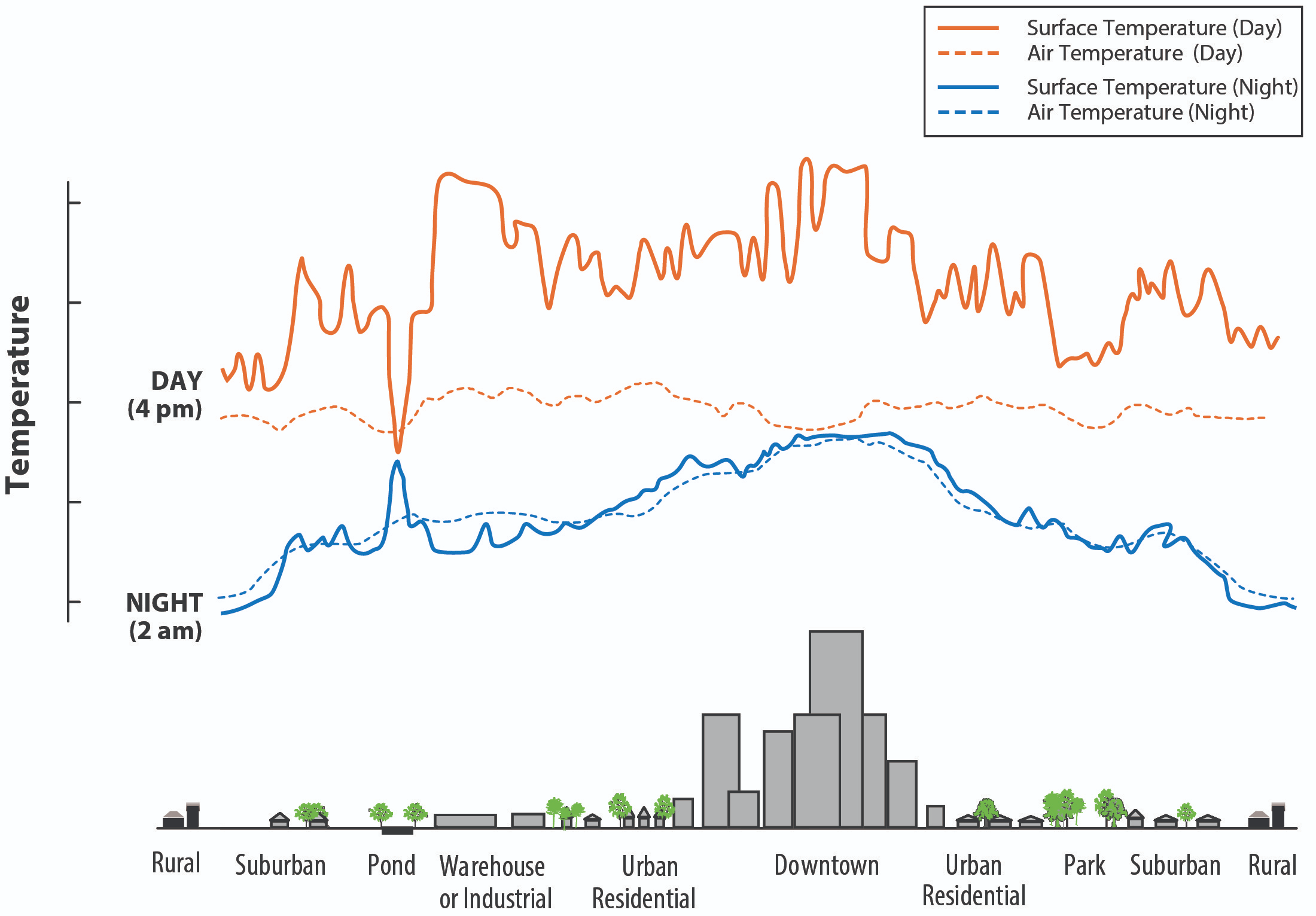
Cross-section of an urban heat island showing hotter downtown surfaces and relatively cooler vegetated or water areas, by day and night. This visual explains why dense, paved districts stay warmer and how intra-urban temperature differences arise. Source.
Resource Depletion
Non-renewable Resources
The Earth’s resources are finite, and many essential materials are being depleted at an alarming rate.
Fossil Fuels: Oil, coal, and natural gas are being consumed faster than they can be replaced. The depletion of these energy sources is not only an energy crisis but also a significant contributor to climate change due to the emission of greenhouse gases.
Minerals: Essential minerals like copper and lithium are finite and face depletion. These minerals are crucial for modern technology and energy solutions, including renewable energy sources.
Renewable Resources
Even resources that are considered renewable are facing challenges.
Overfishing: Fish populations are declining due to excessive fishing practices. The depletion of fish stocks threatens marine ecosystems and the livelihoods of communities dependent on fishing.
Deforestation: Forests are being cut down for timber, agriculture, and urban development at unsustainable rates. This loss of forests contributes to biodiversity loss, climate change, and disrupted water cycles.
Technological Solutions and Limitations
Technology offers potential solutions but also presents its own challenges.
Innovation: While technology can enhance efficiency and discover alternatives, it requires significant investment and time. The pace of innovation must accelerate to meet the growing demands.
E-waste: The rapid pace of technological advancement leads to an increase in electronic waste. Managing and recycling e-waste is a growing concern, contributing to pollution and health issues.
Climate Change
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The increase in greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) is a significant driver of climate change.
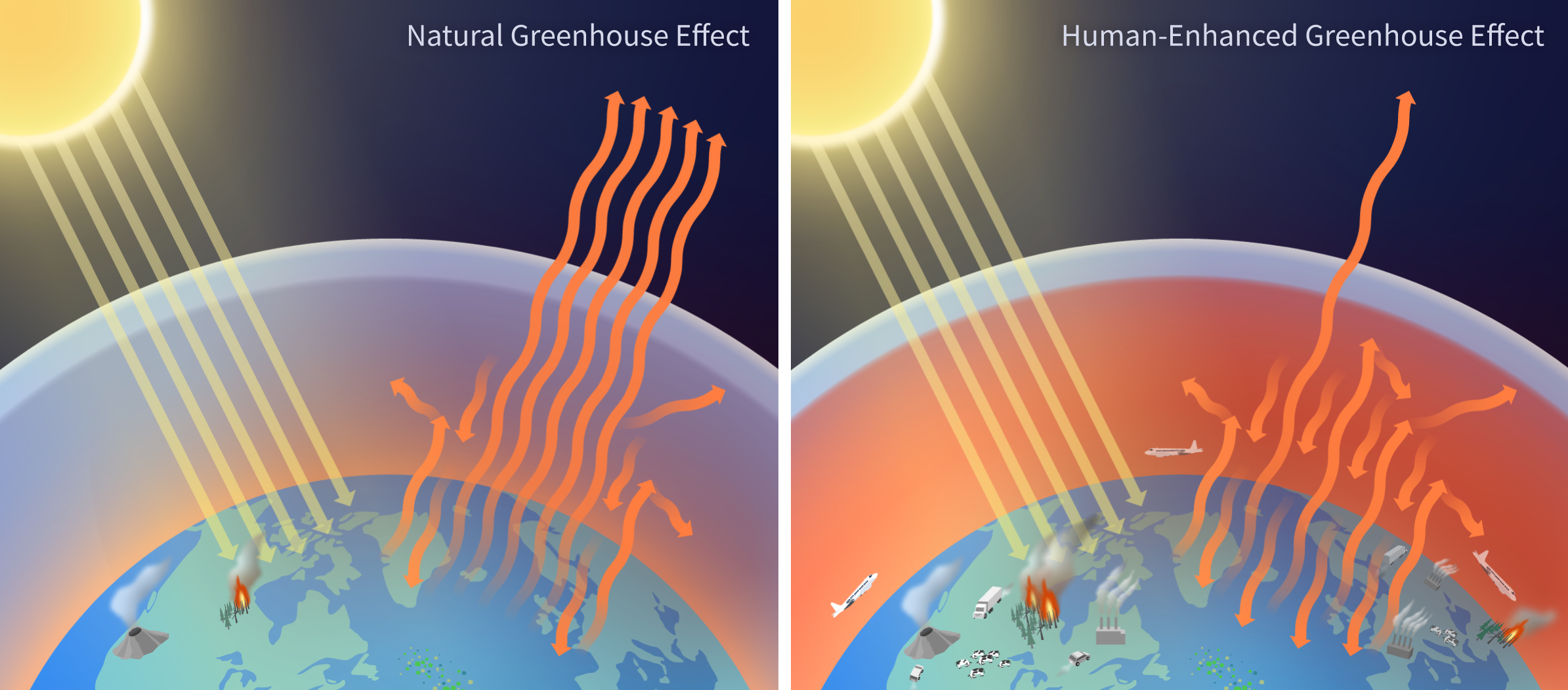
Left: Earth’s natural greenhouse effect traps some outgoing infrared radiation and keeps the planet habitable. Right: Human-released greenhouse gases intensify this effect, increasing the energy retained by the climate system. Source.
Industrial Processes: Factories, transportation, and energy production release vast amounts of CO2. These emissions are a primary driver of the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming.
Deforestation: The removal of trees reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb CO2, exacerbating the greenhouse effect and contributing to climate change.
Impacts of Climate Change
The effects of climate change are diverse, affecting various aspects of the environment and human society.
Weather Patterns: There is an increased frequency and severity of storms, droughts, and floods. These extreme weather events lead to loss of life, property damage, and food and water shortages.
Sea Level Rise: Melting ice caps and glaciers lead to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities with flooding and erosion.
Adaptation and Mitigation
Addressing climate change requires both adaptation to the changes that are already occurring and efforts to mitigate future impacts.
Policy: Implementing policies that reduce emissions and promote sustainable practices is crucial. International agreements like the Paris Agreement aim to unite countries in the fight against climate change.
Technology: Developing technologies to reduce greenhouse gases and adapt to changing conditions is essential. Innovations in renewable energy, carbon capture, and climate-resistant crops are examples of technological solutions.
Interconnected Challenges
Complex Relationships
The challenges to sustainability are not isolated; they are interconnected and complex.
Population and Climate Change: Population growth increases energy demand, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions. This connection amplifies the impacts of climate change.
Resource Depletion and Population: More people lead to increased consumption, accelerating resource depletion. This relationship exacerbates the strain on the Earth’s finite resources.
Holistic Approaches
Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive, holistic approaches.
Policy Integration: Policies must address multiple challenges simultaneously, considering the complex relationships between them. Integrated approaches can lead to more effective and sustainable solutions.
Global Cooperation: International collaboration is essential to tackle global issues like climate change and resource depletion. Unity in action can lead to shared solutions and resources to combat these challenges.
Future Perspectives
Technological Innovation
Advancements in technology offer hope for overcoming sustainability challenges.
Alternative Energy: The development and adoption of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal are crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on finite resources.
Sustainable Practices: Innovations in agriculture, waste management, and industrial processes to reduce environmental impact are essential for achieving sustainability.
Education and Awareness
Increasing awareness and education about sustainability challenges is crucial.
Public Awareness: Educating the public about the impacts of their choices and behaviours can lead to more sustainable lifestyles and consumer demands.
Policy Makers: Ensuring those in power are informed and motivated to take action for sustainable development is essential for implementing effective policies and regulations.
While the path to sustainability is fraught with challenges, understanding these obstacles is the first step towards overcoming them. Each issue, from population growth and resource depletion to climate change, is a piece of a larger puzzle that requires global cooperation, innovative solutions, and informed choices to solve. Through combined efforts, a sustainable future can be forged, ensuring the Earth remains a hospitable home for all its inhabitants.
FAQ
Economic factors are significant contributors to the challenges of achieving sustainability. The global economy often prioritises short-term gains over long-term environmental health. For example, industries might opt for cheaper, yet environmentally harmful practices to reduce costs and maximise profits. This can lead to overexploitation of natural resources, pollution, and environmental degradation. Additionally, economic disparities between nations can hinder global cooperative efforts to address sustainability challenges. Wealthier nations often have more resources to invest in sustainable practices, while poorer nations may struggle to implement such measures, leading to uneven progress towards global sustainability.
Policy and legislation are crucial tools in addressing sustainability challenges by establishing legal frameworks that govern individuals, communities, and industries’ interactions with the environment. Effective policies can enforce sustainable practices, restrict environmentally harmful activities, and incentivise the adoption of green technologies. For instance, policies can mandate emission reductions for industries, enforce conservation efforts, and promote the sustainable management of natural resources. However, the effectiveness of these policies often depends on comprehensive design, strict implementation, and international cooperation to address global environmental issues like climate change and resource depletion.
Consumer behaviour significantly influences the challenges to sustainability. The demand for goods and services drives industrial activities, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental pollution. For example, high demand for fast fashion contributes to waste generation and pollution due to the rapid production and disposal of clothing. Similarly, a preference for convenience items, like single-use plastics, exacerbates plastic pollution. Educating consumers about the environmental impacts of their choices and promoting sustainable consumption habits, such as reducing waste, opting for sustainable products, and supporting eco-friendly companies, can mitigate these challenges and contribute to sustainability.
Both individual actions and systemic changes are vital for overcoming challenges to sustainability. Individual actions, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, and supporting sustainable products and companies, contribute to the collective effort to mitigate environmental impacts. Every action counts, and widespread adoption of sustainable habits can lead to significant positive effects. However, systemic changes are also essential to address the root causes of sustainability challenges. These include reforms in policy, industrial practices, and economic structures to enforce sustainable development, resource conservation, and emission reductions on a larger scale. The combination of individual efforts and systemic changes offers the most comprehensive approach to achieving sustainability.
The loss of biodiversity exacerbates the challenges to sustainability by weakening ecosystems and reducing their resilience to environmental changes. Biodiversity is integral for ecosystem health, providing stability, resilience, and adaptability. A diverse ecosystem can better withstand environmental stresses and is more likely to recover from disturbances. For instance, biodiversity contributes to soil fertility, water purification, and pollination, all essential ecosystem services that support human survival and well-being. The loss of biodiversity, often due to habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, undermines these services, escalating the challenges of ensuring resource availability and ecosystem health for a growing global population.
Practice Questions
Population growth amplifies sustainability challenges by increasing the demand for resources and escalating environmental degradation. A larger population requires more food, water, and energy, leading to intensified agricultural activities, water extraction, and energy consumption. For instance, increased agricultural activities can lead to deforestation and loss of biodiversity. Additionally, a larger population produces more waste, including plastics and greenhouse gases, exacerbating pollution and climate change. Urbanisation, another consequence of population growth, results in the expansion of cities, increasing the strain on infrastructure and leading to environmental issues like air and water pollution.
Technological innovation plays a pivotal role in mitigating sustainability challenges posed by resource depletion and climate change. For resource depletion, technology aids in the development of alternative materials and more efficient extraction methods, reducing the strain on finite resources. For example, advancements in battery technology are reducing dependence on finite lithium supplies. In the context of climate change, technological innovations, such as renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, are instrumental in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon capture and storage technologies are examples of innovations that mitigate the effects of emitted greenhouse gases, contributing to climate stabilisation.

