Sustainability is a multifaceted concept that seeks to ensure the well-being of current and future generations. It encompasses a balanced approach, integrating economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection to achieve a harmonious and resilient world.
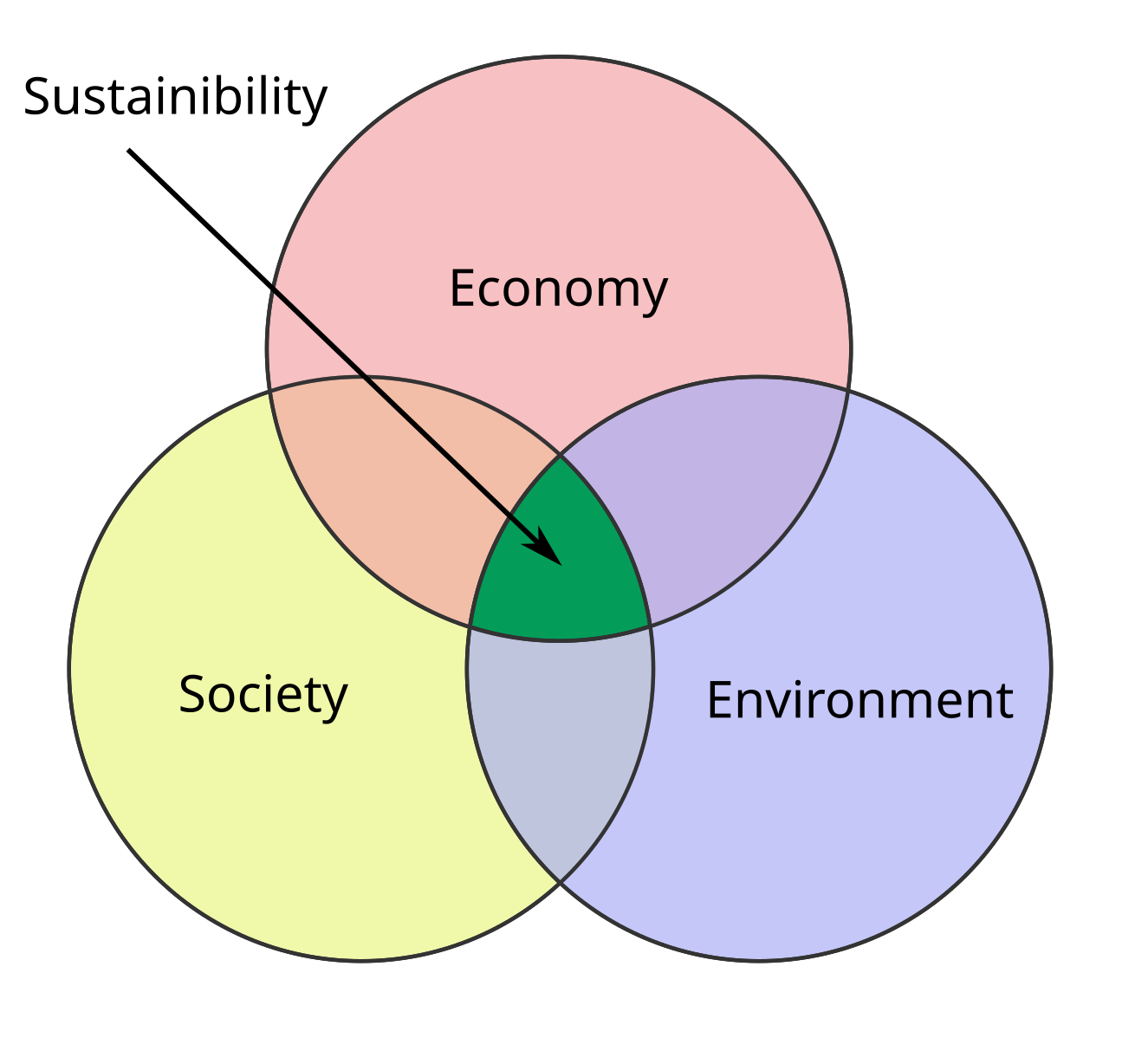
This diagram shows the three pillars—environmental, social and economic—and their overlap as “sustainability,” emphasising interdependence and co-benefits. It reinforces why policies must integrate all three domains to be effective. Source.
The Three Pillars of Sustainability
Economic Sustainability
Resource Management
Economic sustainability is anchored in the principle of efficient and equitable resource management. It underscores the necessity of utilising resources in a manner that minimises waste and maximises value.
Efficient Utilisation: This involves the optimal use of resources to ensure that they serve the greatest number of people while reducing waste. It is about making the most out of available resources through technologies and practices that enhance efficiency.
Innovation: Innovation plays a pivotal role in economic sustainability. It fosters the development of new technologies and methods that enhance resource efficiency, reduce waste, and create alternatives to non-renewable resources.
Equity: Equity is about ensuring that the economic benefits and resources are distributed fairly across society. It seeks to bridge the gap between the rich and the poor, ensuring that everyone has access to the resources and opportunities they need to thrive.
Long-term Focus
A long-term focus is essential in economic sustainability. It involves making decisions and investments that not only benefit the present generation but also future generations.
Prudent Investment: This involves allocating resources to projects and initiatives that promise long-term benefits. It underscores the importance of foresight in investment decisions, prioritising projects that are sustainable and beneficial in the long run.
Risk Management: Economic sustainability also involves identifying and mitigating risks that could lead to economic downturns. It requires policies and strategies that safeguard the economy against shocks and stresses, ensuring stability and resilience.
Social Sustainability
Human Rights and Equality
Social sustainability is rooted in the principles of human rights and equality. It seeks to create societies where everyone’s needs are met, and rights are respected.
Access: This principle ensures that all individuals have access to basic needs and services, including healthcare, education, and housing. It is about removing barriers that hinder people from accessing the services they need to live a dignified life.
Diversity: Social sustainability celebrates and respects cultural and social diversity. It recognises the richness that diversity brings to society and seeks to promote inclusivity and respect for all.
Participation: Participation underscores the importance of involving everyone in societal affairs. It fosters a sense of belonging and ownership, where people are actively involved in shaping the decisions that affect their lives.
Health and Education
The health and education of the population are central to social sustainability. They are foundational to the well-being and productivity of any society.
Well-being: This principle focuses on the holistic well-being of individuals, encompassing physical, mental, and social aspects. It seeks to create conditions that enhance the quality of life for all.
Knowledge: Education and knowledge are pivotal in empowering individuals and communities. They foster informed and skilled populations capable of contributing meaningfully to societal progress.
Environmental Sustainability
Conservation
Environmental sustainability is about conserving and protecting the natural environment to ensure it continues to support life on Earth.
Biodiversity: This principle underscores the importance of preserving diverse ecosystems, species, and genes. Biodiversity enhances the resilience and adaptability of the environment.
Ecosystem Services: These are the natural processes and systems that support life on Earth. The principle seeks to maintain and enhance these services, ensuring that the environment continues to support life.
Pollution and Waste
Reduction: This principle is about reducing pollution and waste through efficient practices and recycling. It seeks to minimise the negative impacts of waste on the environment.
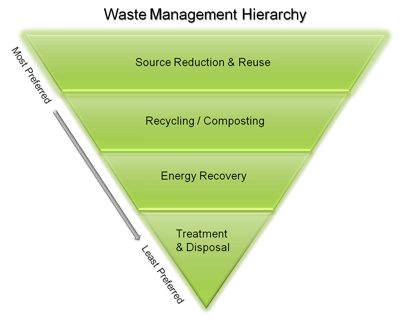
An inverted-triangle diagram from the U.S. EPA ranks waste management options, placing source reduction and reuse above recycling, energy recovery and disposal. This visual supports the priority order for minimising environmental impacts and aligns with policy-led waste regulation. Source.
Regulation: Implementing and enforcing regulations is crucial in protecting the environment. This principle underscores the role of policies and laws in safeguarding environmental integrity.
Balancing the Pillars
Integration
Policy Making: Policies that consider economic, social, and environmental aspects are crucial. They ensure a balanced approach to development, where no aspect is overlooked or sacrificed for another.
Stakeholder Engagement: This involves various stakeholders to ensure diverse perspectives are considered. It fosters inclusivity and comprehensive solutions to sustainability challenges.
Adaptation and Flexibility
Learning: This principle underscores the importance of continuously learning and adapting to new challenges and opportunities. It fosters a dynamic approach to sustainability, where strategies and actions evolve in response to emerging insights and challenges.
Resilience: Building the capacity to withstand and recover from various shocks and stresses is central to sustainability. It ensures that societies and ecosystems can bounce back and thrive amidst challenges.
Case Studies and Examples
Circular Economy
Design Thinking: Products are designed for durability, reuse, and recyclability, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Business Models: Businesses adopt models focusing on service provision rather than product ownership, promoting resource efficiency and reduction of waste.
Community Engagement in Urban Planning
Inclusivity: All community members, including marginalised groups, are involved in the planning process, ensuring diverse needs and perspectives are considered.
Social Capital: Building social networks and relationships enhances community well-being and fosters a sense of belonging and cooperation.
Renewable Energy Transition
Technology: Advancements in technology are making renewable energy more accessible and affordable, driving the shift away from fossil fuels.
Policy: Government policies incentivise the adoption of renewable energy sources, accelerating the transition to cleaner and sustainable energy.
Challenges and Opportunities
Complexity
Sustainability is complex and multifaceted, requiring a holistic and integrated approach to address interconnected challenges associated with economic, social, and environmental sustainability.
Collaboration
Collaboration among governments, businesses, communities, and individuals is essential. It requires shared values, mutual respect, and the collective will to bring about meaningful change.
Innovation
Innovation in technology, policy, and social systems is a driving force that can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable world. It opens up new opportunities and pathways for addressing sustainability challenges, fostering a world where economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection coexist harmoniously for the benefit of current and future generations.
FAQ
The integration of the three pillars of sustainability influences international policy making by fostering a holistic approach to global challenges. Policies are designed to balance economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection to achieve sustainable development. International agreements and treaties, such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), exemplify this integration, addressing a range of issues from poverty alleviation and quality education to climate action and life below water. Such comprehensive policies ensure that international development initiatives are multifaceted, addressing the complex and interconnected challenges that global societies face in a balanced and equitable manner.
Governments are pivotal in promoting environmental sustainability through the formulation and implementation of policies and regulations. They set legal frameworks and standards that govern the use of natural resources, waste management, pollution control, and conservation efforts. For instance, policies that mandate reduced emissions, ban harmful practices, or incentivize the use of clean technologies contribute to environmental protection. Governments also play a role in international collaborations to address global environmental issues like climate change. By enforcing regulations and promoting sustainable practices, governments can steer societies towards a path of environmental stewardship and sustainability.
The principles of sustainability provide a framework to mitigate the challenges of rapid urbanisation. Economic sustainability ensures that urban development is accompanied by job creation, wealth distribution, and efficient resource utilization to support the growing population. Social sustainability focuses on enhancing the quality of life, including housing, healthcare, education, and social inclusion to cater to diverse urban populations. Environmental sustainability in urban contexts involves managing waste, reducing pollution, conserving green spaces, and implementing eco-friendly urban planning to mitigate environmental degradation. Thus, applying sustainability principles in urban development ensures that cities are livable, resilient, and capable of supporting their populations effectively.
Social sustainability principles are instrumental in addressing inequality and promoting social justice. They advocate for equal access to resources, opportunities, and basic services for all individuals, regardless of their social, economic, or cultural background. By promoting inclusivity and diversity, social sustainability ensures that the voices and needs of marginalized and underrepresented groups are acknowledged and addressed. Policies and initiatives that focus on education, healthcare, and social services are essential in empowering individuals, enhancing their well-being, and enabling them to contribute meaningfully to societal development. Thus, social sustainability fosters a just and equitable society where everyone can thrive.
Businesses play a crucial role in achieving economic sustainability by adopting practices that are both profitable and environmentally friendly. Implementing eco-friendly operations, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, and minimizing emissions, can lead to cost savings and enhanced efficiency. Additionally, businesses can innovate to develop products or services that are not only marketable but also environmentally sustainable. For instance, adopting circular economy principles, where products are designed for durability, reuse, and recyclability, can reduce environmental impact while creating economic value. Thus, aligning business strategies with environmental conservation leads to a win-win scenario of economic growth and environmental protection.
Practice Questions
The three pillars of sustainability are intricately linked, each playing a pivotal role in achieving a balanced and resilient world. Economic sustainability ensures efficient and equitable resource management, fostering growth that is inclusive and beneficial to all. Social sustainability focuses on human rights, equality, and well-being, ensuring that societal structures support the holistic development of every individual. Environmental sustainability is about conserving and protecting the natural environment, ensuring it continues to support life. Each pillar impacts the others; for instance, economic growth can affect social well-being and environmental health. Hence, a balanced integration of all three pillars is essential for holistic sustainability.
Innovation and technology are catalysts for both economic and environmental sustainability. Economically, innovations enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. They foster the development of new methods and technologies that maximise resource use, reduce waste, and open up new economic opportunities. In the environmental context, innovations contribute to the development of cleaner and more sustainable technologies. For instance, advancements in renewable energy technologies are reducing dependence on fossil fuels, mitigating pollution, and conserving natural resources. Thus, innovation and technology are instrumental in transitioning towards a more sustainable economic and environmental paradigm, marked by efficiency, conservation, and resilience.

